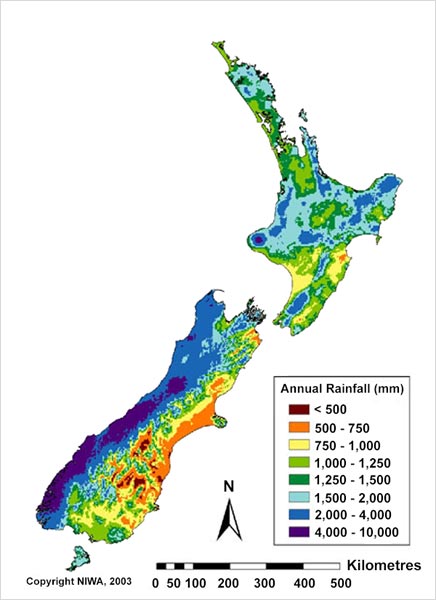
The distribution of New Zealand’s ample rainfall is greatly affected by the mountains. In general, the east is drier and the west is wetter. The mean annual rainfall varies from less than 500 millimetres in Central Otago to over 6,000 millimetres at Milford Sound (in the south-west South Island). Most areas receive 600–1,500 millimetres per year, but large areas of both islands receive over 2,500 millimetres.
New Zealand has small areas of higher rainfall, which can’t be seen on a map of this scale, such as a narrow band on the Southern Alps that gets 10,000 millimetres of rain per year. The highest recorded annual rainfall was over 18,000 millimetres, measured at Cropp River on the West Coast.
Te whakamahi i tēnei tūemi
NIWA – National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research
This item has been provided for private study purposes (such as school projects, family and local history research) and any published reproduction (print or electronic) may infringe copyright law. It is the responsibility of the user of any material to obtain clearance from the copyright holder.



Tāpiritia te tākupu hou